Dynamic bending of the IEA 15 MW reference wind turbine blade
In this benchmark problem we examine the transient flapwise tip response of the IEA 15 MW reference wind turbine blade (using the IEA-15-240-RWT definition in WindIO format) subjected to a concentrated tip load. The blade structural properties (reference axis, twist distribution, and sectional 6x6 mass and stiffness matrices) are read directly from the WindIO YAML file and mapped to a Legendre Spectral Finite Element (LSFE) beam model with \(n = 11\) nodes. The blade is clamped at the root, and a point force \(P_z = -200\) kN is applied at the tip node in the global \(z\)-direction (i.e., flapwise direction) to simulate a wind loading condition. This load is large enough to cause a significant deflection of the tip node (approximately 20% of the blade length of ~118 meters), which is important for testing the accuracy of the nonlinear response of the geometrically exact beam element.
The transient response is computed with Kynema’s dynamic solver using a generalized-\(\alpha\) time integrator with numerical damping parameter \(\rho_\infty = 0.4\), a time-step size of \(\Delta t = 0.001\) s, and a total simulated time of 10 seconds. BeamDyn is used to provide a benchmark solution for the same blade model, loading, and time-integration parameters. The tip out-of-plane displacements from Kynema are compared against the BeamDyn benchmark solution in the following figure. The comparison shows good agreement, with Kynema results lying within 1% relative difference of the BeamDyn displacements over the vast majority of the response history.
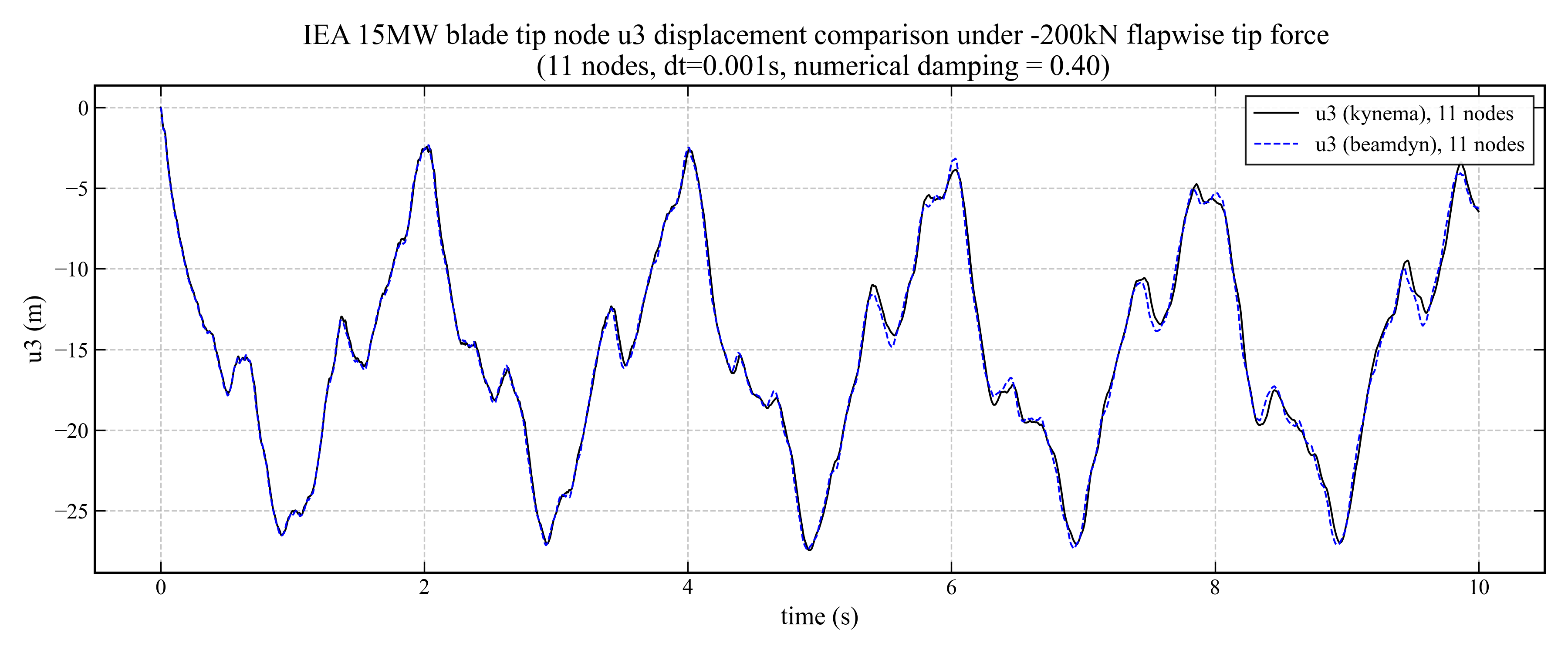
9 Comparison of tip flapwise displacement (\(u_3\)) for the IEA 15 MW reference blade between Kynema and BeamDyn for a single LSFE model with \(n = 11\) nodes under a tip load of \(-200\) kN, with a time-step size of \(\Delta t = 0.001\) s.
Note
This benchmark is included as a regression test in the Kynema code base. The test is implemented in: